Going Edge with Cloud...

What is Edge Computing?
Wikipedia says:
"Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed to improve response times and save bandwidth."
It's self-explanatory but let's take an example to simplify it. Suppose, you want to create an account in a Bank and for that, you need to visit its main branch which is 600 kms away from your location. Would you do that?
No one would come that far until there're selling diamonds for free!
To solve this, Bank has created a branch which is located just 4 kms away from you. So you would just visit the branch and all your work will be replicated to the main branch within no time.
The same will happen in Edge Computing. When the application is hosted in the US and a user is requesting data from India then just think how much travel the request needs to do. Instead, user requests will be forwarded to the nearest server. That server will process the required operations and responds with what the user needs.
The main goal behind Edge Computing is to minimize the latency by bringing the servers closest to the Edge. It can make difference when a real-time response is required. Just think about Self-Driving Car. It can't even tolerate a milli-second latency.
Advantages:
Here are some advantages we get from Edge Computing:
- Real-time response: Response in some use-cases like Self-driving car is a critical factor
- Reliability: Edge devices don't need to be continuously connected to the internet. It can store results locally and sends them to the cloud whenever the internet is available.
- Limited Data Exposure: Sensitive data won't go outside of the client location.
- Lesser Network Load: Only limited data will be sent to the Cloud as most of the operations happens at Edge.
Edge computing can be used in many scenarios like SmartCity projects, IoT, Intelligent Hospitals, Live Broadcasting, Intelligent Parking, etc.
Too many theories! Let's see Practical
Now, let's take an example of how you can use the power of cloud computing with Edge Computing.
Let's say you have an Object Detection Algorithm that you want to deploy for multiple clients on their sites. Deployment is fine until you have a limited number of clients. But when the number grows, you need to manage multiple Edge sites, handle continuous upgrades, check for data durability, and whatnot.
How would anyone handle 1000 separate locations! You're kidding me, right?
I have a solution. We can use Public Cloud like AWS or Azure.
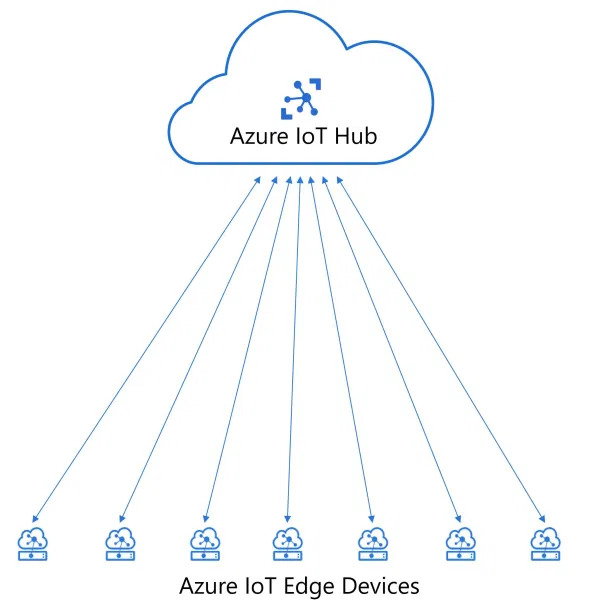
To implement in Azure, we can use Azure IoT Edge. We can configure
Azure IoT Hub to monitor and manage all the Edge Devices. We can deploy our applications
to selected Edge Devices within few minutes. All these things with just minimal
configurations in Edge Devices.
Ultimately, lots of things under one dashboard.
Similarly, Amazon Web Services also provides IoT Core services. Our usecase can be implemented using AWS IoT Core and GreenGrass.
Sounds interesting?
I would love to explain how it can be done. Here, I am sharing few existing great articles for step by step guide on setting up this scenario. Why reinvent the wheel!
- Object Detection with Azure IoT Edge
- Getting started with IoT Edge
- AWS Greengrass the forefront of edge computing
Did you like what you read? Recommend this post to others!
Want to share something? I would Love to hear from you!